Written by: Erica Bartlett, Control Systems Resource Manager with Linda Ricard
Published October 2024
Transforming disparate operation and communication systems into a smart, automated, wireless mesh industrial network takes meticulous planning, detailed engineering, and extensive knowledge of wireless hardware, fiber optic installation best practices, and communication protocols.
While Wireless Plant Networks (WPN) have been shown to improve industrial operations from an efficiency standpoint, their adoption has been limited by the perceived security and reliability risks that these wireless systems can present. Today’s highly robust, reliable, and ruggedized wireless technologies are rapidly advancing to address these cybersecurity risks with stringent IIoT security features to keep hackers out while also supporting the evolving industrial applications of tomorrow.
Currently, the main justification cited for moving to wireless technologies is to give engineers and operators the ability to monitor, manage, and maintain equipment in the field without being confined to an office or control room. The ability to access live plant data and current drawing records on their tablets during field walks saves time and money.
Once the infrastructure is installed, WPNs open up enormous opportunities that can give operators the ability to install wireless devices for maintenance applications (i.e., condition or event monitoring) without the expense of control wiring or capacity limitation issues. Edge devices can also be used to take advantage of cloud services and applications.
Real-Time Actionable Intelligence
The goal of an Industrial WPN is to securely transfer information across multiple sensors, wireless transmitters, smart gateways, and networks within the WPN to meet ISA 100 (Wireless Systems for Automation requirements). The resulting real-time data can provide operators with heightened situational awareness. With this information, operators can quickly resolve issues, even from outside of the control room. This cost-effective and efficient approach to delivering mission critical data gives operators the ability to run their units more efficiently for better uptime.
Self-Organizing Mesh Technology Ensures Reliable Communications
One of the core benefits of WPN is reliable communications. Wireless devices with antennas and sensors send data to a gateway. If an issue with a device occurs along the way, the information is subsequently rerouted by forming a new path through another device to continue transmission to the gateway.
Architecting a Wireless Plant Network
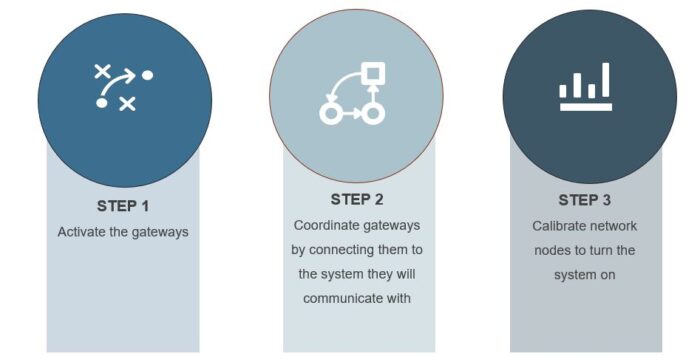
Developing a WPN requires installing up to hundreds of wireless network nodes (i.e., access point (AP) devices), in various locations throughout an industrial plant or refinery to enable instrumentation to communicate with either a Process Control Network (PCN) or business/IT network. Acting like routers, APs then communicate back to a central control room via fiber, network switches, wireless network controllers, and wireless device managers. Building a wireless system requires activating, coordinating, and calibrating devices and gateways in the system.
Once all of the APs in a production plant or refinery are connected to each other, the constellation of devices can then transfer sensor data across the spectrum of industrial communication systems, significantly improving the speed, agility, and stability of Wi-Fi systems. The system is designed to maximize the capacity of the radio frequency (RF) spectrum and radio range performance while minimizing network overhead and RF signal losses.
Did You Know …..
Security features, like multi-layered protection, RF security, WLAN intrusion prevention, network access control, and encryption, are hardwired into each AP device. Gateway firewalls meet the Achilles communications certification. Encryption algorithms meet NIST FIPS 197 industry requirements. These stringent security features keep hackers from breaking into the network.
A robust WPN delivers high levels of fault tolerance in multi-node configurations, regardless of which nodes might fail. If any device fails, the rest of the devices continue to communicate with the central control room via the PCN. APs are built to maintain power as they are hardwired to the power supply in addition to having backup batteries. APs can also withstand extreme temperatures of -40° F to +150° F and humidity conditions for ruggedized and reliable performance.
In addition, a WPN does not age like typical equipment due to its modular design, making it easy for owners/operators to replace and/or upgrade components or insert new technologies over time.
Three Major Considerations to Building a Wireless Automated Infrastructure
There are three major considerations to building an automated, wireless plant network across an entire spectrum of industrial plant operations: AP device locations, fiber optic connection points, and power sources.
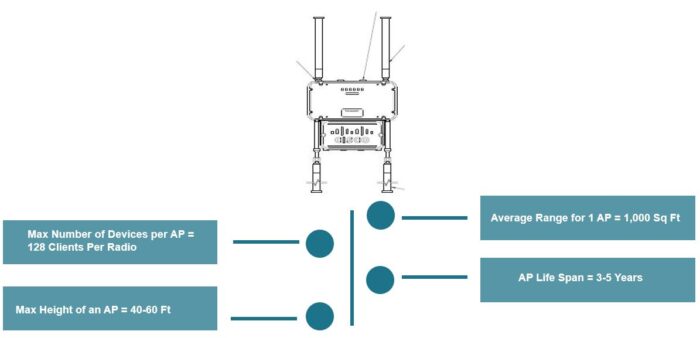
Wireless Mesh AP Device Locations. A solid foundation for a wireless infrastructure requires proper wireless mesh access point (AP) device locations. Wireless AP manufacturers first conduct a site survey to determine where to install the AP devices for full coverage across a production facility and/or outdoor sites. To extend device signals, manufacturers calibrate APs at a higher frequency or install repeaters as point-to-point wireless bridges between two APs.
Facility owners/operators and engineering teams then analyze the resulting information to see if there are obstacles, co-channel and external signal interferences, building layout complications, device height and accessibility issues, and potential security vulnerabilities that may impact placement of the devices.
After analyzing all of the data, they are then able to determine viable AP site locations in the field and how to minimize the number of devices needed while also providing maximum coverage across the area.
Fiber Optic Connection Points. Another major factor to take into consideration from a cost perspective regards fiber optic connection points. Installing new fiber optics to connect the wireless access point devices to a control room can drastically increase project costs, as is the case with refinery tank farms that require extremely long fiber optic runs.
Power Sources. Finding power sources for all the IT/OT hardware listed above is also important for the success of the wireless infrastructure projects. However, this consideration is typically not as difficult to accomplish as the first two.
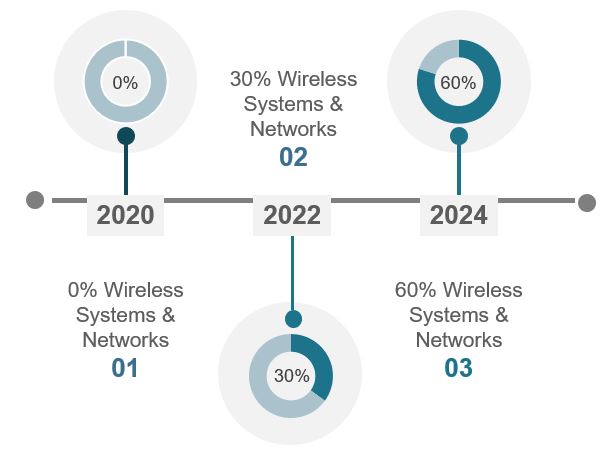
More and more refinery owners are rapidly integrating their operations into wireless systems and networks as seen in the following example.
Example of Rapid Deployment of Wireless Installations Across an Oil & Gas Owner’s Multiple U.S. Refineries in a Four-Year Period
Reducing Risk in Wireless Installations
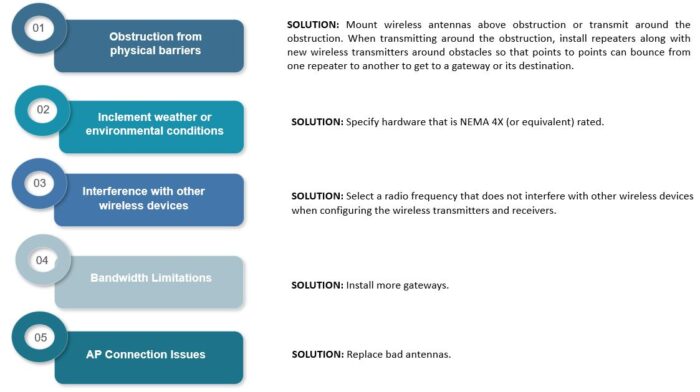
Wireless signal strength can be impacted by the following issues:
Summary
Installing an industrial WPN is now becoming a viable option for refinery owners/operators because of advanced technologies, accepted industry standards, and improvements in cybersecurity. WPNs provide refinery operators with more sensor data and control outside of the control room. By monitoring and managing equipment performance on tablets in the field, operators can better maintain their equipment over time.
A wireless network creates a new infrastructure with new capabilities that operators can take advantage of. A WPN’s plug and play capability gives operators the flexibility to cost effectively insert new technologies over time. This ensures that the infrastructure will continue to evolve and grow into the future.
Download and view the full whitepaper here →